Sunday, 14 June 2020
AIR KNOCKER
Saturday, 13 June 2020
TYPES OF FLANGES
Flanges can be classified in different ways as follows:
1. Based on Type of Connection:
a) Threaded Flanges:
These types of flanges also called as "Screwed flanges", because these flanges having a thread inside the flange bore. The thread inside the flange bore which fits on the pipe which is having a matching male thread on the pipe. The main advantage of this flanges is that they can be attached to the pipe without any welding. In some cases a seal weld is also used in combination with a threaded connection. This type of joint connection and dismantling is speedy and also simple but for high pressure and temperature applications these are not suitable. It is also not suitable for a pipe system with thin wall thickness because thread cutting on a pipe of thin wall thickness is not possible so we have to choose pipe with thicker wall thickness.
b) Socket-weld Flanges:
Socket-Weld Flanges features a female socket in which pipe is fitted. Generally Socket-weld flanges are used for small size (NPS 2 and smaller) and high pressure piping systems. These flanges static strength is equal to slip on flanges.
The connection is done by inserting pipe into the recess area and 1 fillet weld is done from outside on the pipe. Before creating the welding, we need to create some space between the flange and pipe.
To reduce the residual stress at the root of the weld that could occur during solidification of weld metal bottom clearance is given in the socket weld. In the bottom image X measures the expansion gap.
Disadvantages:
1. Maintain specific gap.
2. Cracking problems between the flange and pipe by corrosive products can cause problems.
c) Slip on Flanges:
SPILLWAY
Friday, 12 June 2020
Fan Pump or Split-Case Pumps | | Use of Fan Pump in Paper Making Plant | |
 |
| Image Courtesy: Https://www.pattersonpumps.com |
Use of FAN PUMP in Paper Plants:
The finished slurry is diluted in silo with white water. The fan pump propels this diluted slurry for paper making towards the headbox. These pumps have been designed to reduce the pulsation, since the pump goal is to maintain constant weight overtime and avoid "Baring". At the inlet of the fan pump, thick stock, generally 3 to 5% consistency is diluted with white water. At the delivery end of the fan pump, the consistency of thin-stock around 0.3 to 1% solids. Mixing action of chemicals like fillers, acids and bases by paper makers before the fan pump happen within the fan pump.
Wednesday, 22 April 2020
STEAM TRAPS & TYPES OF STEAM TRAPS
Types of steam traps: Based on working principle
Mechanical Steam Traps:
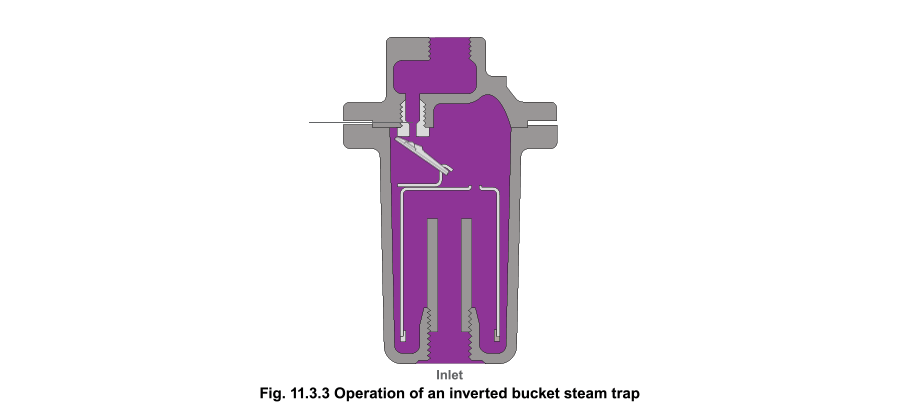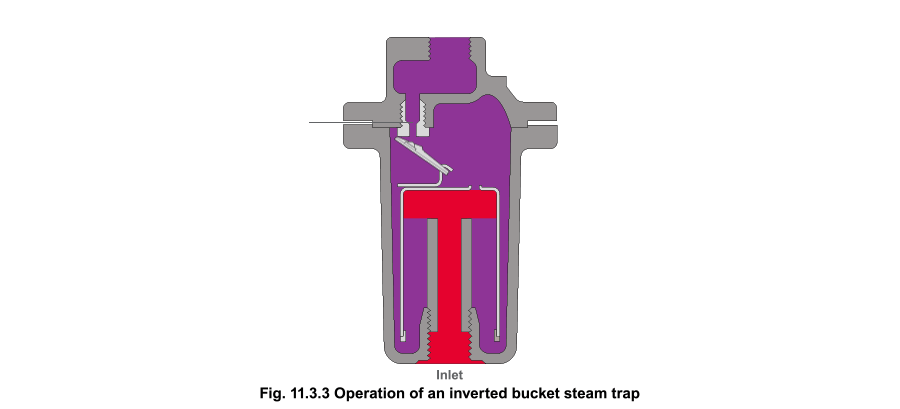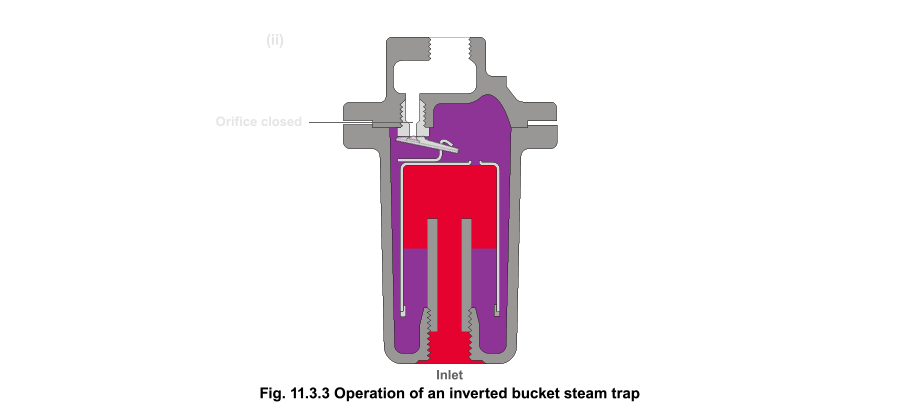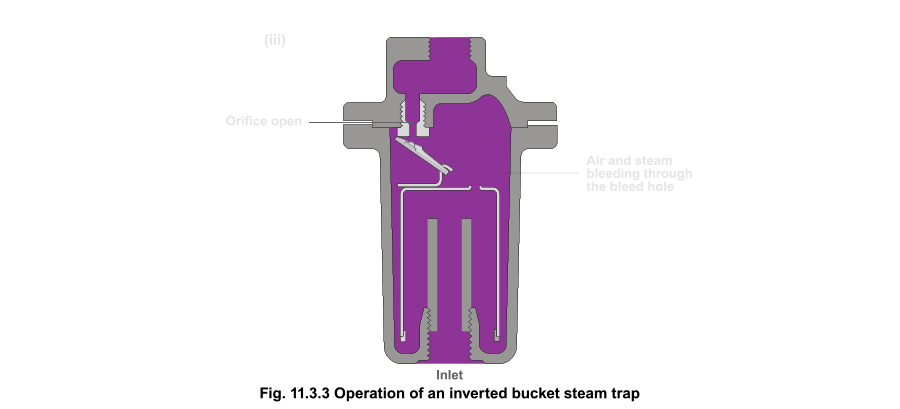
Float-and-Thermostatic:
Thermodynamic (or) Disk type:
Thermodynamic, (or) Disk-type, steam traps use a flat disk that moves between the cap and the seat (See Figure). Initially, condensate flow raises the disk and opens the discharge port. Steam or very hot condensate that enters the trap applies pressure on the disc and seats the disk. It remains seated, closing the discharge port, until there is pressure is maintained above it. Heat radiates out through the cap, thereby diminishing the pressure on the disk, opening the trap to discharge condensate.Wear and dirt are particular problems that we face with a disk-type trap. Due to the large, flat seating surface, any particulate contamination such as dirt or sand, lies between the disk and the valve seat. This prevents the valve from sealing and allows live steam to flow through the discharge port. If pressure is not maintained above the disk, the trap will operate frequently. This wastes steam and may cause the device to fail prematurely.
The key advantage of these traps is that one trap can handle an entire range of pressures. In addition, they are relatively compact for the amount of condensate they discharge. In these type of traps disk is the only moving part, maintenance can easily be carried out without removing the trap from the line.
The main disadvantage is difficulty in handling air and other non-condensable gases. Thermodynamic steam traps will not work positively on very low pressures.
Bi-metallic type steam traps:
Bi-metallic steam trap works on the same principle as a residential-heating thermostat. As the name indicates, these traps are constructed using two strips of dissimilar metals welded together into one element. The element deflects when heated. A bi-metallic strip, or wafer, connected to a valve disk, bends or distorts when subjected to a change in temperature. When properly calibrated, the disk closes tightly against a seat when steam is present and opens when condensate, air, and other gases are present.The key advantages of bi-metallic traps are (1) Compact size compared to load-handling capabilities and (2) Immunity to hydraulic-hammer damage.
Their biggest disadvantage is the need for constant adjustment (or) Calibration, which is usually done at the factory for the intended steam operating pressure. If the trap is used at a lower pressure, it may discharge live steam. If the trap is used at a higher pressure, condensate may back up into the steam system.










